|
|
Sulkowitch Urine (Calcium) Test |
| Sulkowitch Urine Test kit |
| Sulkowitch Test - high calcium |
| Sulkowitch Test - Low calcium |
|
|
| Water Test Kit (2-test pack) |
| Adrenal Function Urine Test |
| pH Indicators (Calcium) Test |
|
|
|
SULKOWITCH URINE (CALCIUM) TEST KIT
Monitor your health through your urine calcium
High levels of calcium
If the test shows high levels of urine calcium, it may be due to:
- Hyperparathyroidism - when calcium levels are too low, the body responds by increasing production of parathyroid hormone. This increase in parathyroid hormone causes
more calcium to be taken from the bone and more calcium to be reabsorbed by the intestines and kidney. When the calcium level returns to normal, parathyroid hormone
production slows down
- Idiopathic hypercalciuria -Idiopathic hypercalciuria is the most common metabolic abnormality in patients with calcium kidney stones. Subjects with idiopathic
hypercalciuria have a generalized increase in calcium turnover, which includes increased gut calcium absorption, decreased renal calcium reabsorption, and a tendency to lose
calcium from bone. Despite the increase in intestinal calcium absorption, a negative calcium balance is commonly seen in balance studies, especially in patients on a
low-calcium diet
- Cancer - Cancer can cause hypercalcemia when it spreads to the bones and causes the release of calcium from the bone into the blood or when a cancer produces a
hormone similar to PTH, resulting in increased calcium levels
- Kidney failure - Measuring urine calcium can help determine kidney disease, because low calcium is especially common in those with kidney failure. The cause
may be due a high level of calcium in the urine
- Milk-alkali syndrome - is caused by excessive consumption of milk (which is high in calcium) and certain antacids, especially calcium carbonate or sodium bicarbonate
(baking soda), over a long period of time. Calcium deposits in the kidneys and in other tissues can occur in milk-alkali syndrome. Consumption of excessive amounts of
Vitamin D, which is usually added to milk bought at the supermarket, can worsen this condition
- Renal tubular acidosis - proximal renal tubular acidosis is a condition that occurs when the kidneys don't properly remove acids in the urine, leaving the blood
too acidic
- Sarcoidosis - is a disease in which swelling (inflammation) occurs in the lymph nodes, lungs, liver, eyes, skin, or other tissues
- Use of loop diuretics - Loop diuretics are known to promote calcium excretion by the kidney
- Vitamin D intoxication - Vitamin D is a fat-soluble vitamin that helps the body absorb calcium. Fat-soluble vitamins are stored in the body's fatty tissue. Too
much vitamin D can make the intestines absorb too much calcium. This may cause high levels of calcium in the blood. High blood calcium can lead to calcium deposits in soft
tissues such as the heart and lungs. This can reduce their ability to function
Images of Sulkowitch Urine Test Kit
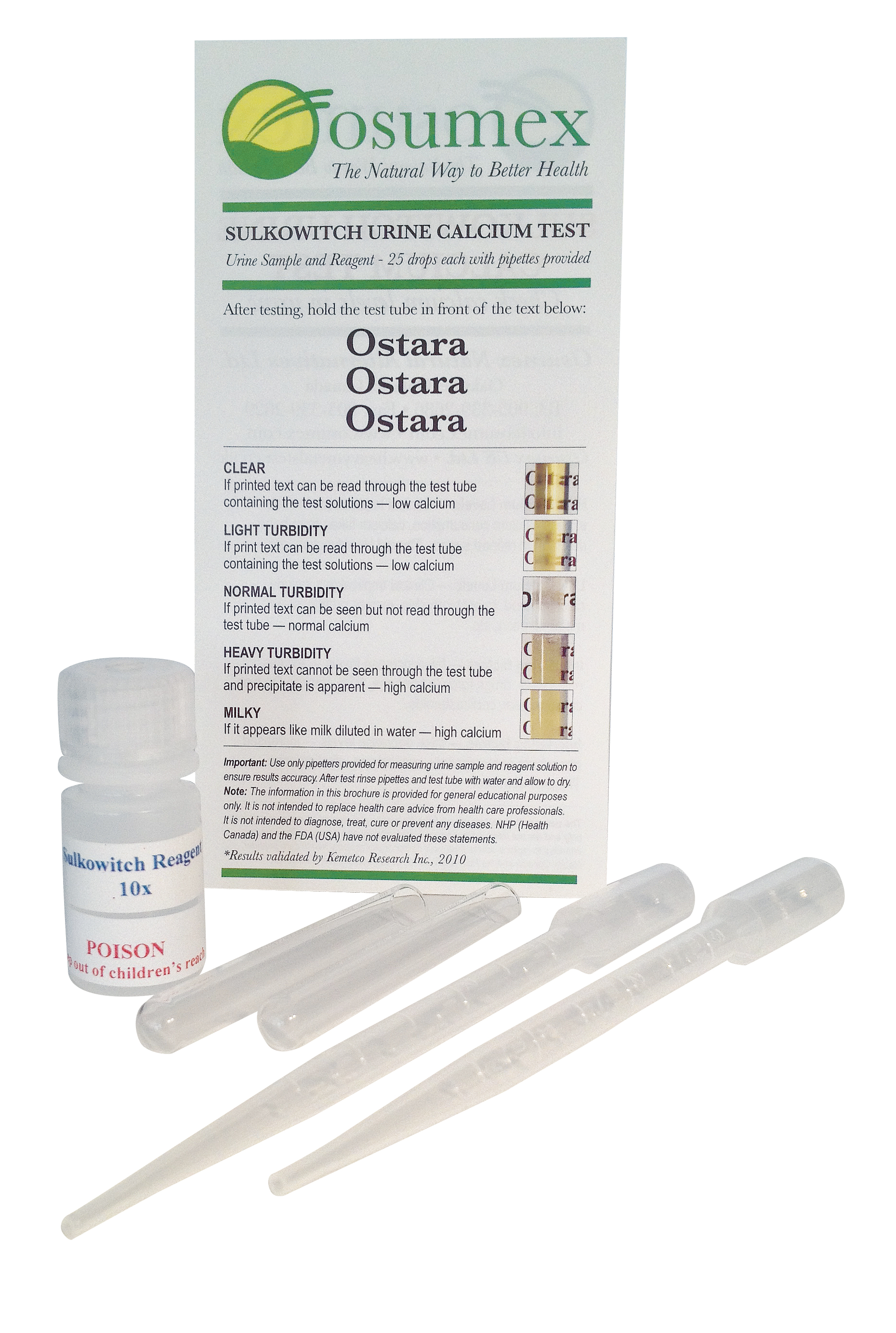 
The Sulkowitch Urine (Calcium) Test was produced in collaboration with and the results were validated by Kemetco Research Inc. based
in Richmond, British Columbia, Canada - 2010

The above information is provided for general
educational purposes only. It is not intended to replace competent
health care advice received from a knowledgeable healthcare professional.
You are urged to seek healthcare advice for the treatment of any
illness or disease.
Health Canada and the FDA (USA) have not evaluated these
statements. This product is not intended to diagnose, treat, cure, or prevent
any disease.
|


